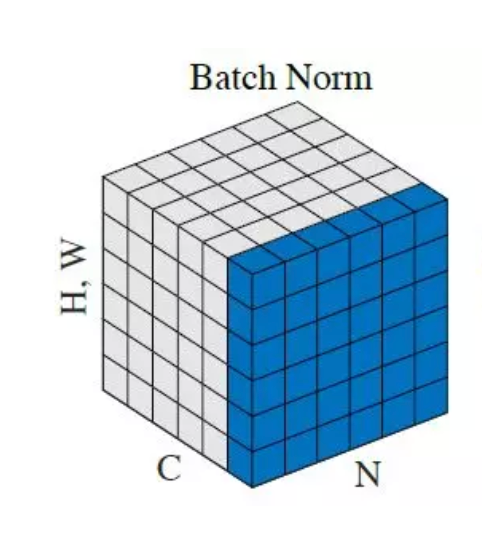
Batch normalisation aims to reduce internal covariate shift, and in doing so aims to accelerate the training of deep neural nets. It accomplishes this via a normalisation step that fixes the means and variances of layer inputs. Batch normalisation also has a beneficial effect on the gradient flow through the network, by reducing the dependence of gradients on the scale of the parameters or of their initial values. This allows for use of much higher learning rates without the risk of divergence. Furthermore, batch normalisation regularises the model and reduces the need for dropout.
We apply a batch normalisation layer as follows for a mini-batch :
Where and are learnable parameters.
References